M -Z
Neuroma
A neuroma is inflammation and thickening of a nerve within the foot, most commonly between the third and fourth toes (Morton’s Neuroma). They are caused by pressure and irritation to a nerve from poorly-fitting shoes, repetitive trauma or abnormal bone structure. Most neuromas are healed with steroid injections, icing, MLS Laser Therapy, and/or alcohol sclerosing injections. These treatments decrease pain and inflammation to the neuroma. Custom orthotics are prescribed to offload the painful area and prevent reoccurrence. If these treatments fail, then surgical removal of the neuroma is sometimes necessary.
Neuropathy (Peripheral Neuropathy)
Peripheral neuropathy is a disease of the nerves within the extremities. It causes loss of the protective sensation to the feet (numbness); including pain, heat, cold, sharpness, and vibration. Ironically, neuropathy can also cause burning, tingling, and shooting pains. This is most commonly due to diabetes, but can also be caused by medications, genetic disease, exposure to heavy metals, trauma, chemotherapy, vitamin deficiency, and more. There are several treatments available for neuropathy depending on cause and symptoms. These include pain creams, medications that act on the nervous system, vitamin B complex supplement, electric nerve stimulation, laser therapy, and blood sugar control.
Plantar Fascitis (Heel Pain)
Plantar fasciitis is a very common condition that causes heel pain. It often occurs with the first steps out of bed or after sitting for extended periods, but can also affect people during their daily activities and sports. The pain can be described as achy, pulling, sharp and/or stabbing. This is due to tightness and inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue across the bottom of the foot. A heel spur may or may not be present and is rarely the source of the pain. This tightness can be caused by flat feet, high arches, obesity, unsupportive shoes, tight calf muscles, fat-pad atrophy, and/or repetitive micro-trauma. The majority of patients with plantar fasciitis improve with conservative (non-surgical) treatment. This includes stretching, rest, appropriate shoe gear, icing, anti-inflammatories, orthotics, avoiding barefoot walking, night splints, steroid injections, MLS Laser therapy, and/or physical therapy.
Sesamoiditis
Sesamoiditis is inflammation and pain to the small, round bones (sesamoids) under the great toe joint, on the ball of the foot. This can be caused by repetitive forces (running), weight gain, and trauma. Treatments include off-loading the painful area with a well-padded surgical shoe or boot, icing, anti-inflammatories, and steroid injections. Once healed, custom orthotic and proper shoe selection may be necessary to prevent reoccurrence. If the sesamoid bone is found to be fractured on x-ray, often times healing does not occur due to the poor circulation to these small bones and surgical excision/removal of the bone is necessary.
Shin splints
Shin splints are pain on either side of the leg bone caused by muscle or tendon inflammation due to over use. It is commonly related to an increase in exercise intensity, excessive foot pronation (collapsing arch), muscle imbalance between opposing muscle groups in the leg, running on different surfaces, and worn out shoes. Treatment includes rest, stretching, icing, anti-inflammatories, and massage. Proper stretching, appropriate shoe gear, and corrective orthotics (shoe inserts) can help prevent shin splints.
Skin Lesions
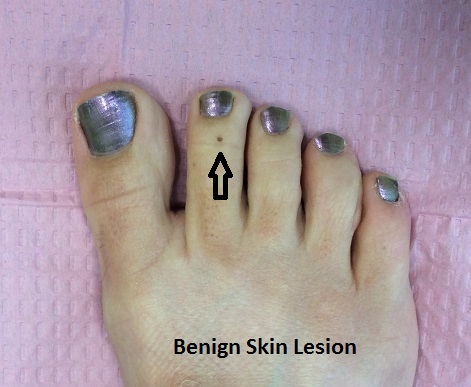 Skin lesions are areas of skin that are different from the surrounding skin. Most skin lesions are benign, such as freckles, moles, pimples, blisters, and rashes. But, it is critical to detect malignant skin lesions, such as malignant melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer. The ABCDEs is a strategy for early recognition.
Skin lesions are areas of skin that are different from the surrounding skin. Most skin lesions are benign, such as freckles, moles, pimples, blisters, and rashes. But, it is critical to detect malignant skin lesions, such as malignant melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer. The ABCDEs is a strategy for early recognition.
A- Benign lesions are symmetrical, malignant lesions are asymmetrical.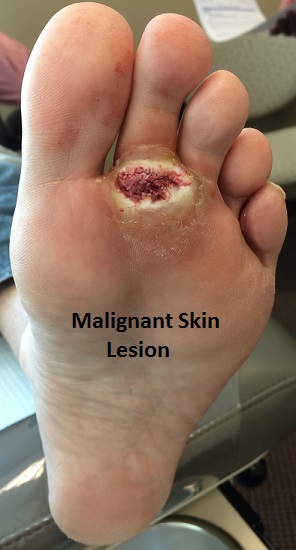
B- Benign lesions have even, smooth borders. Malignant lesions have irregular borders.
C- Benign lesions are usually one color. Malignant lesions have a variety of colors and shades.
D- Benign lesions are usually smaller and malignant lesions are larger.
E- Benign lesions appear the same after time. Malignant lesions change in size, shape, color, elevation, or any other trait. Any new symptom such as bleeding, itching or crusting point to danger.
Stress Fractures
Stress fractures are incomplete cracks in the bone caused by repetitive forces or overuse. Metatarsals are the most common bones in the foot to be fractured. Stress fractures are more prevalent in women and are also associated with poor shoe gear and increased weight and age. Although stress fractures are not complete breaks within the bone, they can be painful and debilitating. Treatment includes rest, icing, anti-inflammatories, compression, and splinting the foot with a surgical shoe or boot. Wearing appropriate shoes for specific activities with quality materials and cushion helps to prevent this condition. Stress fractures left untreated may become complete fractures, which require casting, immobilization, and possible surgical repair.
Swelling
Swelling of the feet, ankles and legs, also called edema, is often caused by an abnormal build-up of fluids within the tissues of the lower extremities. Swelling of the feet and ankles is a common problem, particularly in the elderly population. It may be painful and cause ulcers (sores) or be asymptomatic. Because of the effect of gravity, swelling is particularly noticeable in the feet and lower legs. Swelling can be due to many conditions such as: poor circulation, DVT (deep vein thrombosis or clot), injury, pregnancy, lymphedema (blockage of the lymph system), medications, sitting or standing for long periods of time (airline flights), kidney disease, and cardiac disease. Treatment may include compression dressings, elevation, medications, wound care, and revascularization procedures.
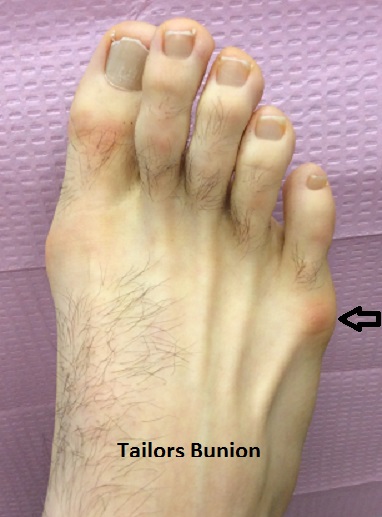
Tailors Bunion
A tailors bunion is a progressive deformity that results from mechanical imbalance and undue stress on the fifth toe (baby toe) joint. This leads to a bony prominence to the outside of the toe joint and drifting of the toe below or above the fourth toe. Contrary to popular belief, bunions are aggravated, not caused, by shoes. Bunions are usually an inherited deformity of the foot. Bunions more commonly affect women due to wearing high-heeled or pointed-toed shoes which aggravate the condition. Symptoms include pain at the fifth toe joint, swelling, redness, corns, calluses, and difficulty wearing shoes due to the increased width of the foot. Because tailors bunions are progressive, it is best to see a podiatrist for diagnosis and treatment to correct the problem before severe pain, arthritis, and deformity occur.
Ulcers (Ulcerations)
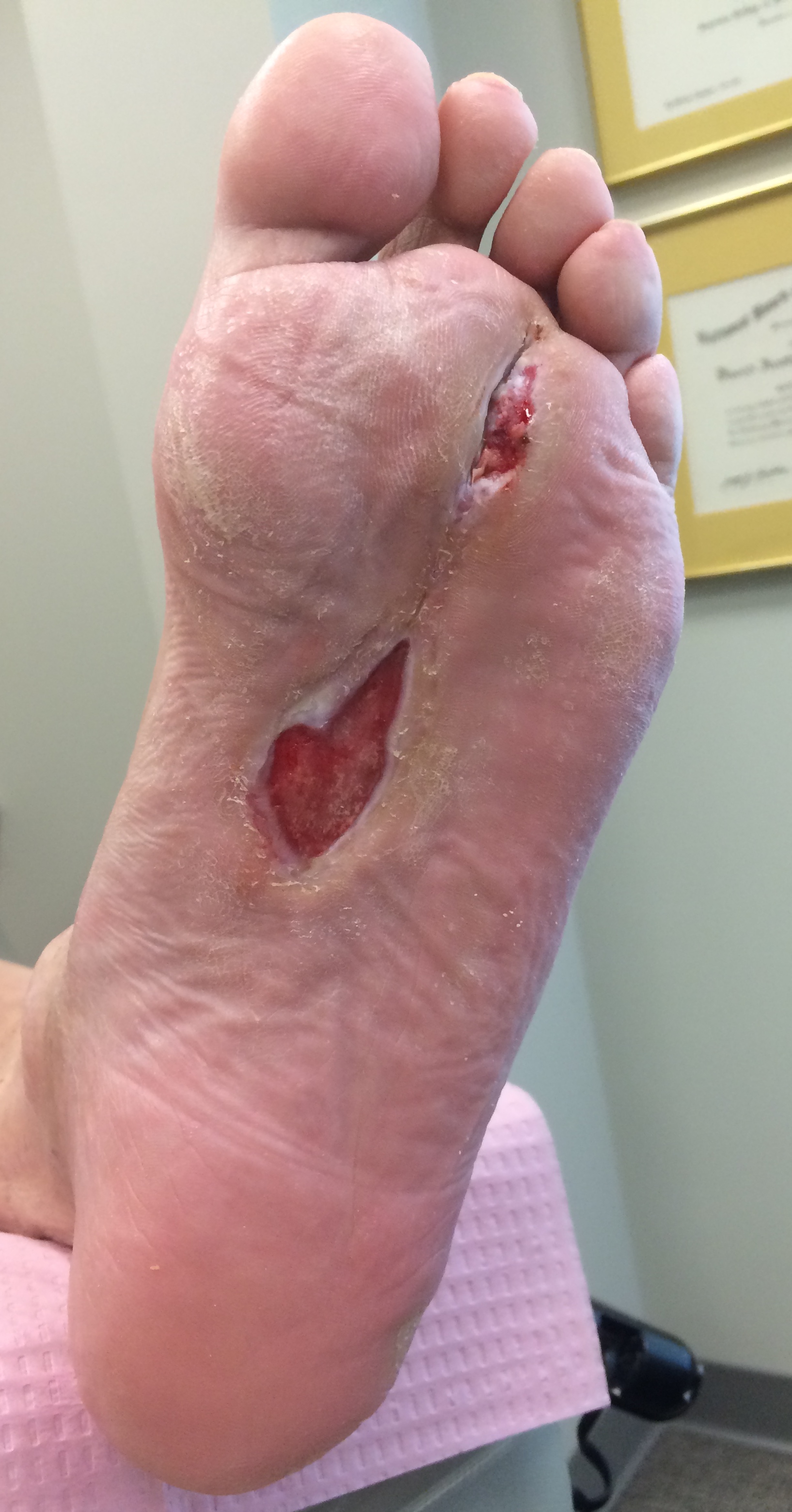 Ulcers are open skin wounds. Ulcers can be found on the feet and legs. They are most common with the diabetic population and those with vascular disease. Ulcers can be very slow to heal due to poor circulation, infection, pressure, increased blood sugars, poor nutrition, and neuropathy (nerve disease). With lack of sensation, something as simple as a splinter or cut on the bottom of the foot can turn into a serious health problem, such as bone infection, sepsis, and amputation. The most important part of treatment is off-loading or taking pressure and weight off of the ulcer. Treatment may also include wound cleaning and debridement (trimming away dead tissue), antibiotics, blood sugar control, hospitalization, consultation with a vascular specialist, and advanced wound care products such as grafts, growth factors, collagen, and negative pressure therapy. Those diagnosed with diabetes or vascular disease should have regular exams and routine foot care by their podiatrist to prevent ulcerations, infections, and amputations. Routine foot care includes examination of the lower extremities, foot care and hygiene education, and trimming of nails and calluses.
Ulcers are open skin wounds. Ulcers can be found on the feet and legs. They are most common with the diabetic population and those with vascular disease. Ulcers can be very slow to heal due to poor circulation, infection, pressure, increased blood sugars, poor nutrition, and neuropathy (nerve disease). With lack of sensation, something as simple as a splinter or cut on the bottom of the foot can turn into a serious health problem, such as bone infection, sepsis, and amputation. The most important part of treatment is off-loading or taking pressure and weight off of the ulcer. Treatment may also include wound cleaning and debridement (trimming away dead tissue), antibiotics, blood sugar control, hospitalization, consultation with a vascular specialist, and advanced wound care products such as grafts, growth factors, collagen, and negative pressure therapy. Those diagnosed with diabetes or vascular disease should have regular exams and routine foot care by their podiatrist to prevent ulcerations, infections, and amputations. Routine foot care includes examination of the lower extremities, foot care and hygiene education, and trimming of nails and calluses.
Warts
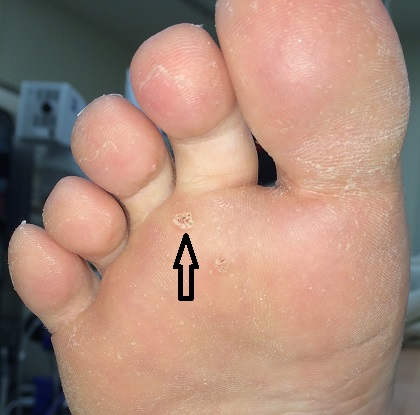 Warts are benign skin lesions due to a viral infection, known as the Human Papilloma Virus (HPV). This generally invades the skin through small cuts and abrasions. They can be painful and are often mistaken for corns or calluses. They can appear anywhere on the skin, but are commonly found on the bottom of the foot (plantar warts). They may be treated with liquid acids, plasters of acid, freezing, vitamins, medications, injections, and laser removal. The greatest success rate is found with laser removal of warts. Approximately 50% of warts may resolve without treatment over a two year period, however, treatment is recommended to prevent spread of the infection to the foot and other people.
Warts are benign skin lesions due to a viral infection, known as the Human Papilloma Virus (HPV). This generally invades the skin through small cuts and abrasions. They can be painful and are often mistaken for corns or calluses. They can appear anywhere on the skin, but are commonly found on the bottom of the foot (plantar warts). They may be treated with liquid acids, plasters of acid, freezing, vitamins, medications, injections, and laser removal. The greatest success rate is found with laser removal of warts. Approximately 50% of warts may resolve without treatment over a two year period, however, treatment is recommended to prevent spread of the infection to the foot and other people.